Blog
07
Jan
2019
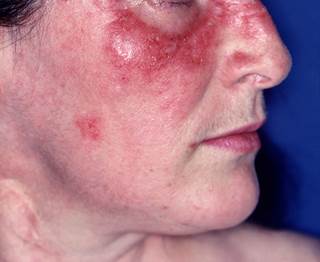
B-Cell Depletion Therapy With Rituximab Effective for Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus